Predicting ICU Admission in Patients With COVID-19
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58445/rars.19Keywords:
Computational Epidemiology, Disease Detection and Diagnosis, Coronavirus Disease 2019, Public Health, Machine LearningAbstract
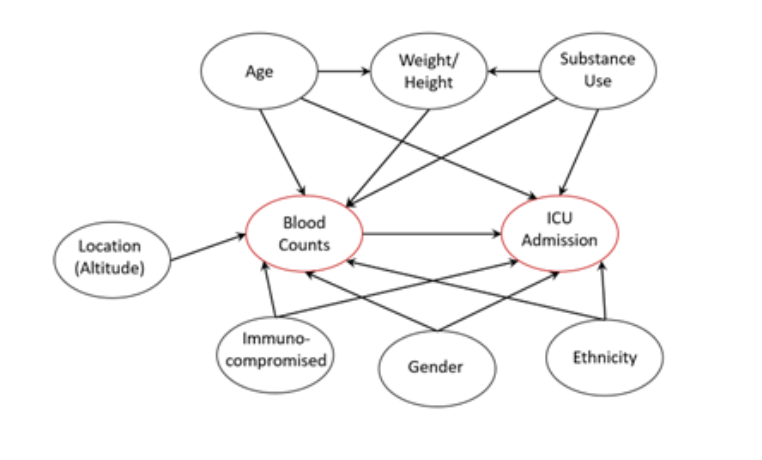
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a global pandemic, affecting the lives of many and challenging unprepared healthcare systems. Due to its recency, there is still much that is unknown about the virus. Blood cell counts as a reflection of virus infection and recovery have played a vital role in COVID-19 immune response, however their correlation with symptom severity has yet to be thoroughly explored.
In this study, the blood counts, and various demographic factors of 383 samples were studied. Anonymized patients in this sample had data collected from Hospital Sírio-Libanês, São Paulo, Brazil. This data was analyzed to determine likelihood of intensive care unit (ICU) admission in patients with COVID-19 based on the blood counts of hemoglobin, platelets, linfocitos (lymphocytes), leukocytes, and neutrophiles, as well as four relevant covariates: body tewmperature, age, gender, and immunocompromised status. From the model, it was determined that neutrophile and leukocyte counts had the greatest predictive influence on ICU admission, while age and immunocompromised status had the least.
With the findings of this study, doctors and other medical health professionals can use the counts of various blood factors in parallel with data on basic relevant covariates to predict infection severity in patients with COVID-19.