The Impact of Climate Change on Animal Behavior
The Arctic Marine and Monterey Bay Ecosystems
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.58445/rars.22Keywords:
ecology, marine biology, marine ecosystems, climate change, the Arctic, Monterey Bay, behavioral ecology, animal behaviorAbstract
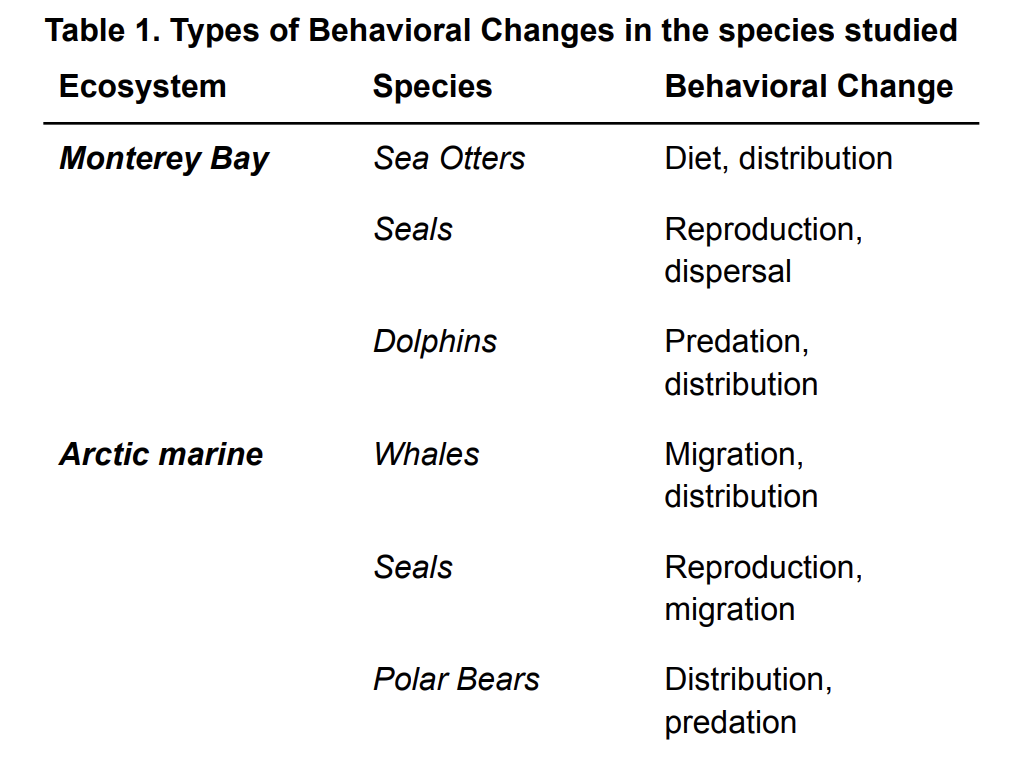
Climate change affects ecosystems worldwide and the entire biosphere. Although the effects of climate change have been well researched, comparisons of its effects on animal behavior across ecosystems are lacking. This study compared the changing behavior of marine mammals in the Arctic marine ecosystem to that in the Monterey Bay ecosystem to narrow this gap. The Arctic marine ecosystem provides habitat for thousands of species, including polar bears, seals, fish, whales, and many species of algae. The Monterey Bay ecosystem, a marine ecosystem located in northern California, is home to hundreds of species of kelp, sea otters, seals, sea lions, seagulls, and other animals. This study highlights the similarities and differences in the migration, predation, distribution, and reproductive behavior of selected animals in response to climate change. This study focuses on species central to each ecosystem: sea otters, seals, and dolphins in Monterey Bay and polar bears, seals, and whales in the Arctic. By accounting for the effects of climate change on animal behavior, predictions were made based on the connection between similar behavioral patterns of the two ecosystems. Through comparing the Arctic marine ecosystem and the Monterey Bay ecosystem, scientists can gain an in-depth understanding of the changes in animal behavior due to climate change across wide geographies and suggest a new method of observing the impact of climate change globally to enable more accurate ecosystem predictions.
Downloads
Posted
Versions
- 2022-12-20 (2)
- 2022-11-16 (1)
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Cecilia Yang

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

